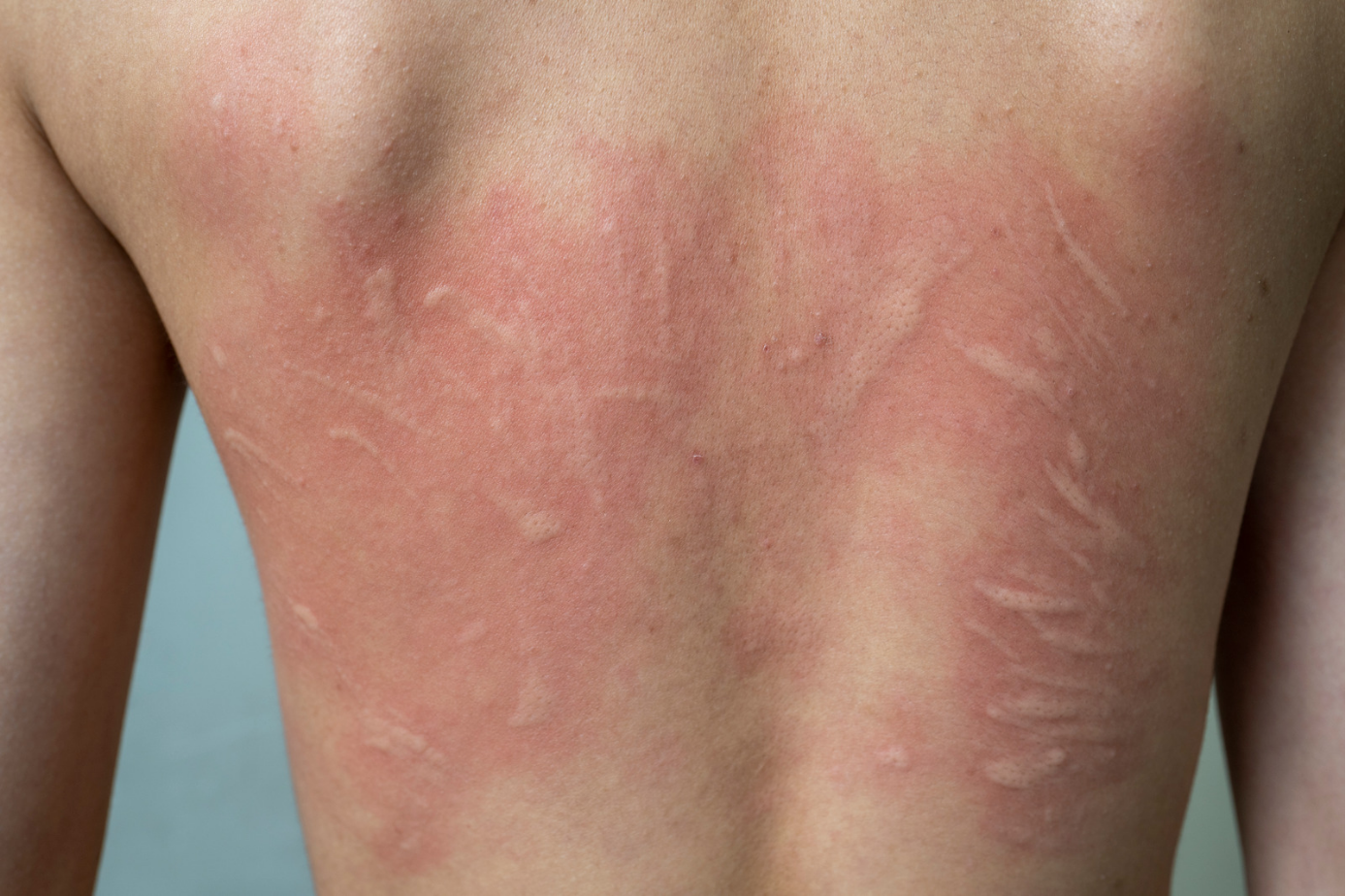
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by red, itchy welts that can appear suddenly and disappear just as quickly. These welts can be triggered by various factors, including allergies, stress, infections, or environmental irritants.
For those who experience urticaria, the question often arises: Can lifestyle changes help prevent it? The answer is nuanced while lifestyle changes may not eliminate urticaria entirely, they can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks for many individuals.
In this article, we’ll explore how diet, stress management, environmental adjustments, and other lifestyle factors can play a role in preventing urticaria, alongside considerations for medical interventions like medications sometimes sourced through cephalexin wholesale for related infections.
Understanding Urticaria and Its Triggers
Before diving into prevention strategies, it’s essential to understand urticaria. Hives occur when the body releases histamine, causing blood vessels to leak fluid into the skin, resulting in raised, itchy patches. Urticaria can be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (persisting longer). Common triggers include:
- Allergens: Foods like nuts, shellfish, or dairy; pollen; pet dander; or medications.
- Physical stimuli: Heat, cold, pressure, or sunlight.
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress can exacerbate symptoms.
- Infections: Bacterial or viral infections may trigger hives in some cases.
- Medications: Certain drugs, including antibiotics or NSAIDs, can cause reactions.
While some triggers, like genetic predispositions, are beyond control, lifestyle changes can address many environmental and behavioral factors, reducing the likelihood of outbreaks.
Dietary Adjustments to Prevent Urticaria
Diet plays a significant role in managing urticaria, particularly for those with food-related triggers. Here are some dietary strategies to consider:
- Identify and Avoid Trigger Foods
Keeping a food diary can help pinpoint culprits like dairy, eggs, or gluten. Elimination diets, guided by a healthcare professional, can confirm sensitivities. For example, some individuals find that cutting out histamine-rich foods—such as aged cheeses, fermented foods, or alcohol—reduces flare-ups. - Incorporate Anti-Inflammatory Foods
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish like salmon or flaxseeds) may help calm the immune system. Turmeric, ginger, and green tea contain compounds that reduce inflammation, potentially lowering the risk of hives. - Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can stress the body, potentially worsening skin conditions. Drinking adequate water supports overall health and may help flush out toxins that contribute to allergic responses.
While dietary changes can be powerful, they require consistency. Consulting a dietitian can ensure nutritional balance while avoiding triggers.
Stress Management for Urticaria Prevention
Stress is a well-documented trigger for urticaria, particularly chronic hives. The body’s stress response can increase histamine release, worsening symptoms. Lifestyle changes focused on stress reduction include:
- Mindfulness and Meditation
Practices like yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can lower cortisol levels, reducing the likelihood of stress-induced hives. Even 10 minutes daily can make a difference. - Regular Exercise
Physical activity boosts endorphins, which counteract stress. However, some people with urticaria triggered by heat or sweat should opt for low-intensity activities like walking or swimming and avoid overexertion. - Adequate Sleep
Poor sleep can heighten stress and weaken the immune system. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep by maintaining a consistent bedtime routine and minimizing screen time before bed.
By prioritizing mental and emotional well-being, individuals can create a buffer against urticaria flare-ups.
Environmental and Hygiene Adjustments
The environment plays a critical role in urticaria prevention. Simple changes can minimize exposure to irritants:
- Control Temperature and Humidity
Extreme heat or cold can trigger hives in some people. Use fans, air conditioning, or heaters to maintain a comfortable environment. Humidifiers can prevent dry skin, which may exacerbate itching. - Choose Gentle Products
Harsh soaps, detergents, or skincare products can irritate sensitive skin. Opt for fragrance-free, hypoallergenic options. When washing clothes, use mild detergents to avoid residue that might cause reactions. - Avoid Known Allergens
If pollen or dust mites trigger hives, use air purifiers, wash bedding frequently, and keep windows closed during high pollen seasons. Pet owners may need to limit exposure to dander by grooming animals regularly.
For those managing infections that could trigger urticaria, medications like antibiotics may be prescribed. In some cases, healthcare providers source these through cephalexin wholesale suppliers to ensure cost-effective treatment for bacterial infections that might exacerbate hives.
Clothing and Physical Habits
What you wear and how you move through the world can influence urticaria:
- Wear Loose, Breathable Fabrics
Tight clothing or rough materials like wool can irritate the skin, triggering hives. Cotton or bamboo fabrics allow the skin to breathe and reduce friction. - Avoid Scratching
Scratching hives can worsen inflammation and lead to infections. Keep nails short and consider antihistamine creams or cool compresses to soothe itching. - Be Mindful of Physical Triggers
For those with pressure-induced urticaria (dermographism), avoid tight belts or heavy bags. If sunlight is a trigger, wear protective clothing and sunscreen.
These small adjustments can significantly reduce irritation and prevent outbreaks.
Medical Support and Lifestyle Synergy
While lifestyle changes are powerful, they often work best alongside medical guidance. For instance:
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter or prescription antihistamines can prevent hives by blocking histamine release. Daily use may be recommended for chronic urticaria.
- Allergy Testing: Identifying specific triggers through skin or blood tests can guide lifestyle changes.
- Infection Management: Bacterial infections, like those treated with antibiotics sourced via cephalexin wholesale, can sometimes underlie hives. Treating the root cause can prevent recurrence.
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting new treatments or making drastic lifestyle changes, especially if symptoms persist.
Limitations and Realistic Expectations
Can urticaria be fully prevented? For some, lifestyle changes dramatically reduce episodes, but complete prevention may not always be possible, especially in chronic cases or those with genetic factors. Triggers like stress or infections can be unpredictable, and even the most diligent efforts may not eliminate hives entirely. However, combining lifestyle changes with medical support offers the best chance for control.
Practical Tips for Long-Term Success
To integrate these changes effectively:
- Start Small: Focus on one area, like diet or stress, and gradually build new habits.
- Track Symptoms: Use a journal to note triggers and improvements, refining your approach over time.
- Seek Support: Allergists, dermatologists, or support groups can provide guidance and encouragement.
By taking a proactive approach, individuals can often reduce the impact of urticaria on daily life.
Conclusion
Urticaria can be a frustrating condition, but lifestyle changes offer a powerful tool for prevention. From dietary tweaks and stress management to environmental adjustments and careful hygiene, small steps can lead to significant improvements. While medical interventions, including antibiotics sourced through cephalexin wholesale for infection-related triggers, may be necessary, lifestyle remains a cornerstone of management. By understanding personal triggers and adopting tailored habits, many people can minimize hives and enjoy greater comfort and confidence in their skin.