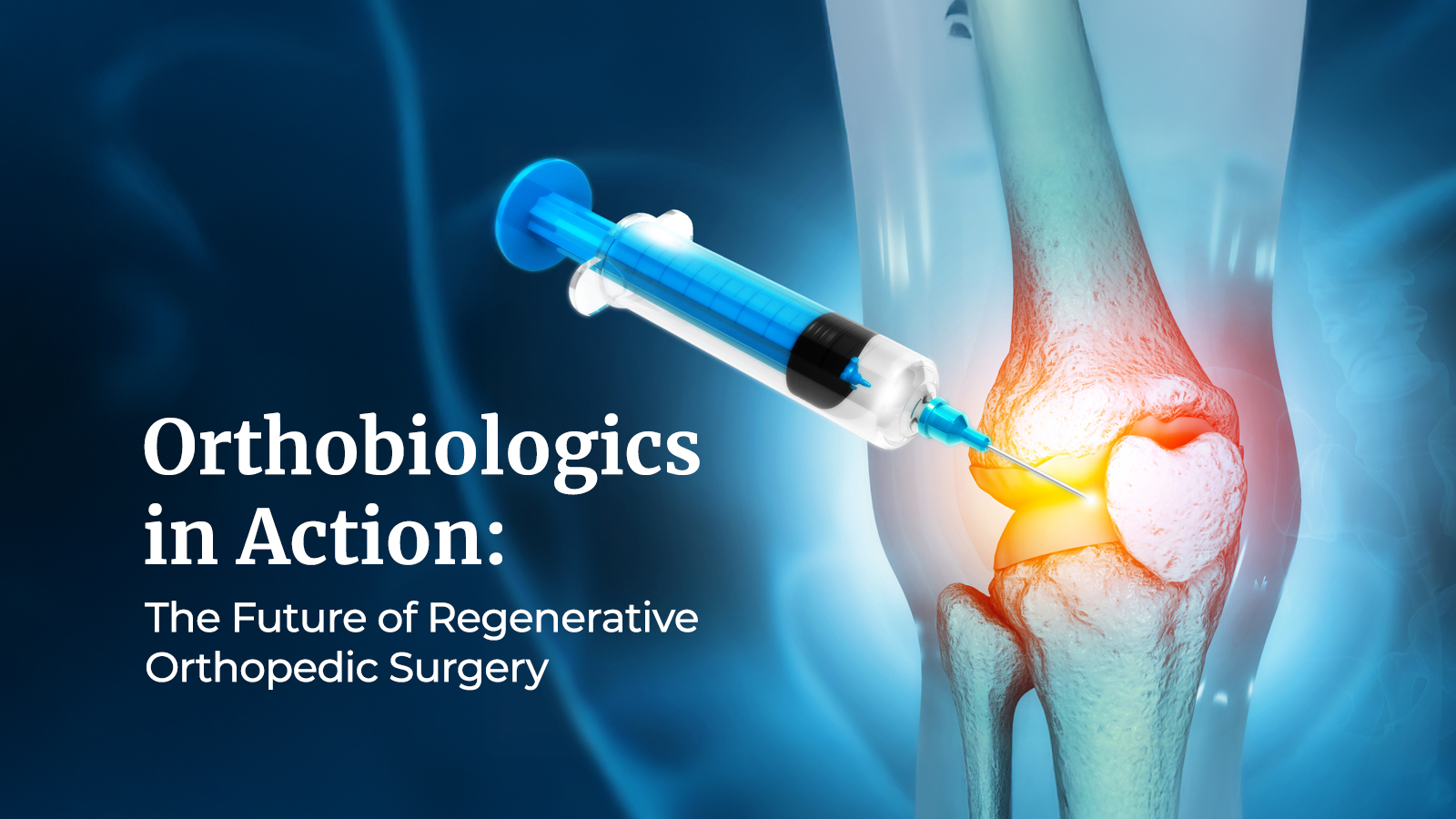
Introduction: A Revolution in Orthopedic Care
Orthopedic surgery has come a long way from traditional bone realignment and joint repair. Today, it is entering a transformative era powered by orthobiologics—biological substances that stimulate and accelerate the body’s natural healing processes. These regenerative therapies are reshaping how orthopedic injuries are treated, offering patients faster recovery, reduced pain, and improved long-term outcomes.
Orthobiologics bridge the gap between medical science and natural healing, creating a future where surgery and biology work hand in hand. As we dive deeper into this innovation, it becomes clear that the future of orthopedic surgery lies not in replacing the body, but in helping it heal itself.
What Are Orthobiologics? The Science of Natural Healing
Orthobiologics refer to biological materials—derived from human tissue or naturally occurring sources—that aid in the repair of bones, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. These materials include platelet-rich plasma (PRP), stem cells, bone marrow aspirate concentrate (BMAC), growth factors, and hyaluronic acid.
When used during surgery or as standalone treatments, orthobiologics boost the body’s ability to heal damaged tissue. Unlike synthetic implants or mechanical repairs, they stimulate natural cell regeneration, offering a biological path to recovery that is safer and more efficient.
How Orthobiologics Work: Merging Biology with Medicine
Orthobiologics work by enhancing the body’s healing response at the cellular level. When an injury occurs, the body naturally sends healing cells and growth factors to the affected site. However, in severe injuries or chronic conditions, this process may be too slow or incomplete. Orthobiologic therapies amplify this natural process by delivering concentrated doses of the body’s own healing materials directly to the damaged area.
For example:
- PRP therapy injects concentrated platelets to release growth factors that trigger tissue repair.
- Stem cell therapy introduces regenerative cells capable of developing into new cartilage, bone, or muscle tissue.
- BMAC treatments provide a mix of stem cells and growth factors to promote faster healing in complex bone and joint injuries.
By harnessing the body’s inherent ability to regenerate, orthobiologics reduce inflammation, repair damaged tissue, and restore function more effectively than traditional methods.
Major Types of Orthobiologic Treatments
1. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves extracting a patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate platelets, and injecting the plasma into the injured site. The platelets release growth factors that stimulate cell regeneration. This treatment is widely used in sports medicine, arthritis, and tendon injuries.
2. Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells are the building blocks of tissue regeneration. They have the unique ability to transform into different types of cells, such as bone, cartilage, or muscle. In orthopedics, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are harvested from bone marrow or fat tissue and used to repair damaged joints or ligaments.
3. Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate (BMAC)
BMAC contains both stem cells and growth factors. It is extracted from bone marrow—typically the hip bone—and reinjected into the affected area. BMAC therapy enhances bone and soft tissue repair and is particularly effective for non-healing fractures.
4. Hyaluronic Acid Injections
Hyaluronic acid, a natural component of joint fluid, acts as a lubricant and cushion. Injecting it into arthritic joints helps reduce pain, improve mobility, and slow the degeneration process.
5. Growth Factors and Biologic Scaffolds
These synthetic or natural materials support tissue regrowth. They are often used during bone grafts, tendon repair, and spine surgeries to improve healing outcomes.
Advantages of Orthobiologics in Orthopedic Surgery
1. Faster Healing and Recovery
Orthobiologics stimulate the body’s repair mechanisms, dramatically shortening recovery time after injuries or surgeries.
2. Reduced Pain and Inflammation
Because these treatments rely on the body’s own healing materials, they promote natural anti-inflammatory responses, minimizing discomfort during recovery.
3. Fewer Surgical Complications
Unlike traditional implants or synthetic materials, orthobiologics are biocompatible and derived from the patient’s own tissue, reducing the risk of infection or rejection.
4. Regeneration Over Replacement
Rather than merely repairing damage, orthobiologics encourage the regeneration of new, healthy tissue—resulting in stronger, longer-lasting outcomes.
5. Potential to Avoid Major Surgery
In many cases, orthobiologic injections can delay or even prevent the need for invasive procedures like joint replacements.
Applications of Orthobiologics in Orthopedic Surgery
Orthobiologics have found their way into nearly every area of orthopedic medicine, including:
- Sports Injuries: Treating ligament tears, muscle strains, and joint inflammation in athletes.
- Spinal Surgery: Enhancing bone fusion and recovery in spinal procedures.
- Fracture Healing: Accelerating bone growth in delayed or complex fractures.
- Cartilage Regeneration: Restoring damaged cartilage in arthritis and joint injuries.
- Joint Preservation: Offering regenerative options before resorting to replacement surgeries.
These treatments are especially valuable in minimally invasive orthopedic surgeries, where biological materials can be applied directly to repair sites, improving recovery without added surgical stress.
Orthobiologics vs. Traditional Orthopedic Treatments
Traditional orthopedic approaches often rely on mechanical intervention—plates, screws, and grafts. While these methods provide structural stability, they don’t address the biological aspect of healing. Orthobiologics add a new dimension by enhancing the body’s biological repair capacity, ensuring that tissues regenerate rather than simply stabilize.
This dual approach—mechanical repair combined with biological enhancement—is setting a new gold standard in modern orthopedic care.
The Future of Orthopedic Surgery with Orthobiologics
The future of orthopedics is deeply intertwined with regenerative medicine. As technology evolves, the next generation of orthobiologic therapies will integrate innovations such as:
- 3D Bioprinting: Creating patient-specific bone and tissue structures.
- Gene Therapy: Modifying cells to promote faster and more targeted regeneration.
- Nanotechnology: Delivering orthobiologic substances more precisely at the cellular level.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Analyzing patient data to personalize regenerative treatments.
These advancements will make orthopedic surgery more precise, minimally invasive, and biologically adaptive, paving the way for personalized regenerative orthopedics—a future where every patient receives a treatment tailored to their unique biology.
Conclusion: Science Meets Healing
Orthobiologics mark a monumental shift in how orthopedic surgeons approach healing. They don’t just repair injuries—they redefine recovery. By combining scientific innovation with the body’s natural regenerative power, orthobiologics create a healing process that is faster, safer, and more sustainable.
From athletes recovering from ligament tears to seniors battling joint degeneration, patients are experiencing the future of medicine today. Orthobiologics stand at the intersection of science and healing, leading orthopedic surgery into a new era of regeneration, restoration, and resilience.